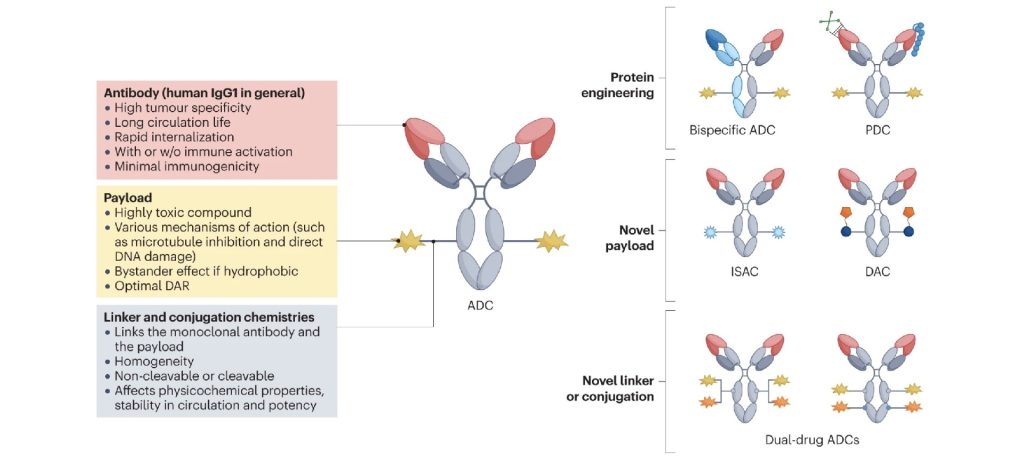
What Is Phage Display?
Phage display leverages the natural biology of bacteriophages—viruses that specifically infect bacteria and archaea—to study protein interactions. Bacteriophages consist of a protein coat that encapsulates either a DNA or RNA genome. Their structural simplicity or complexity varies, but they all share a fundamental ability to inject their genetic material into host cells, making them ideal […]
What Is Phage Display? Read More »