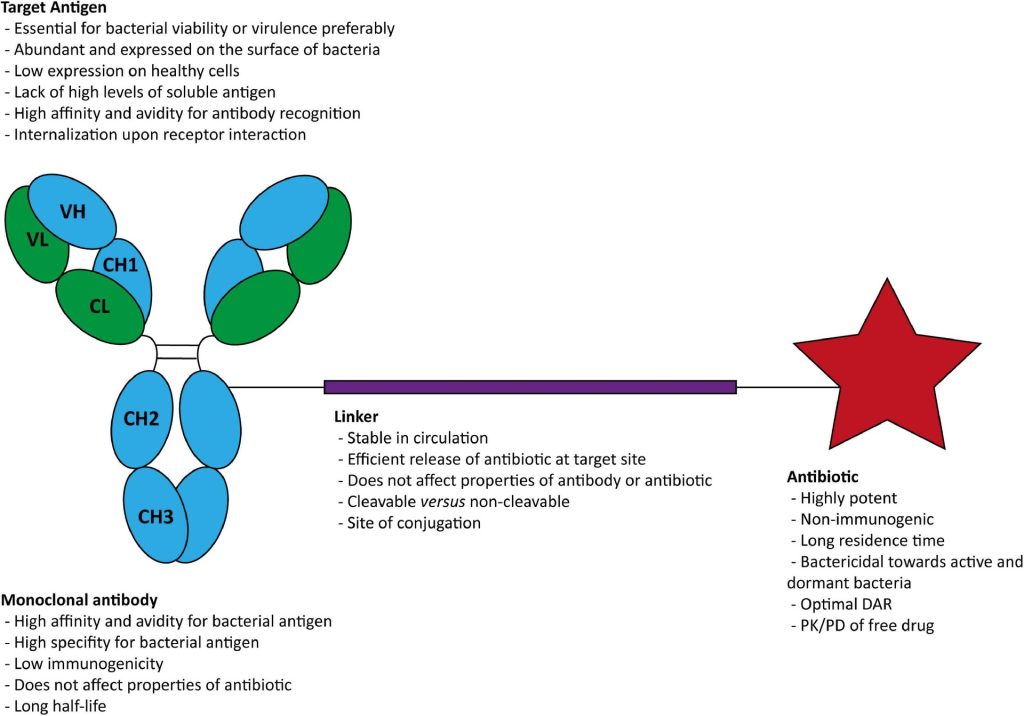
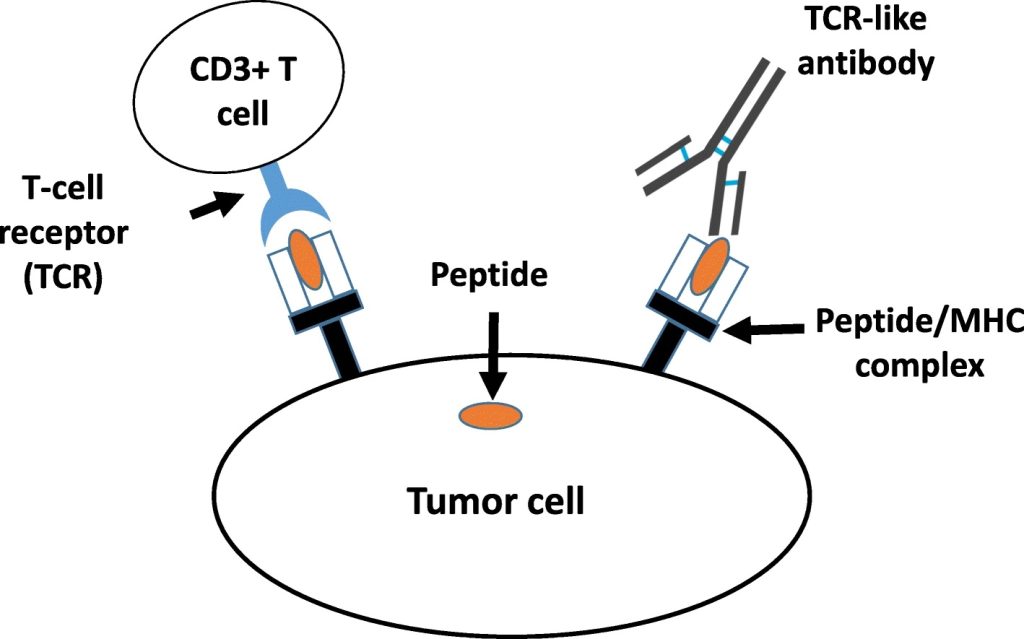
Core Functions of Antibodies
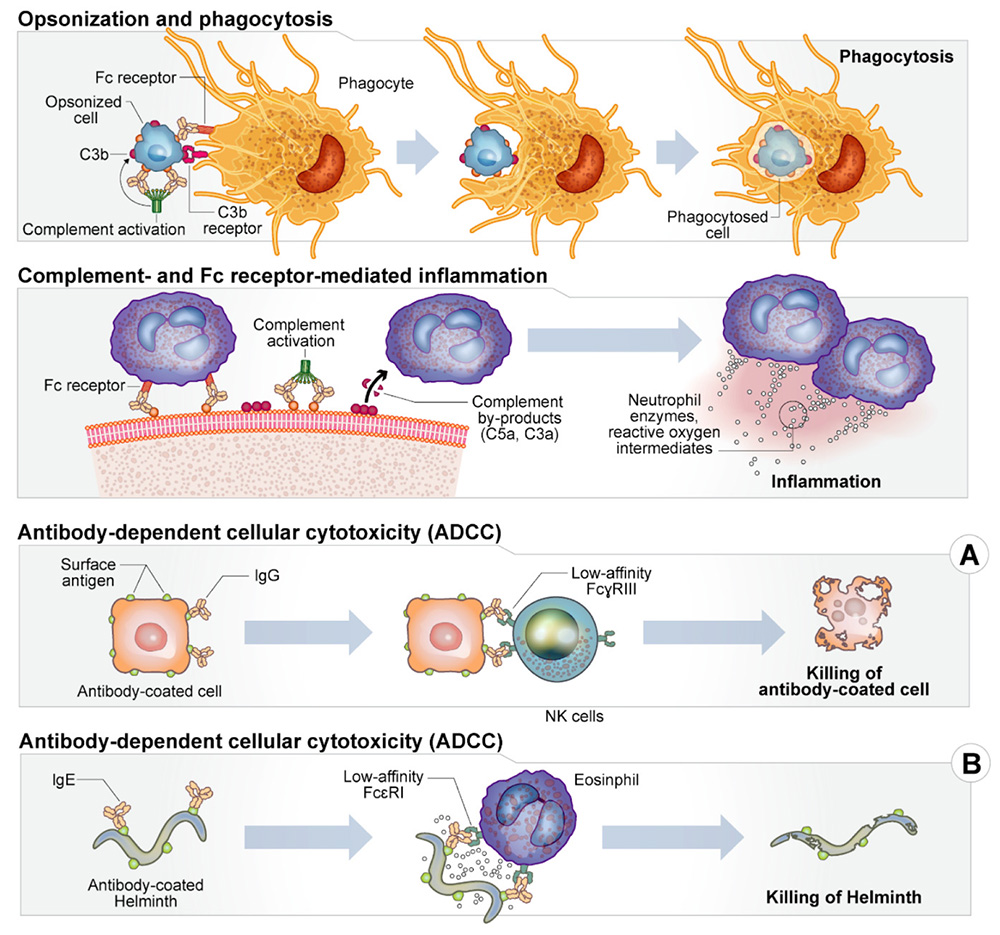
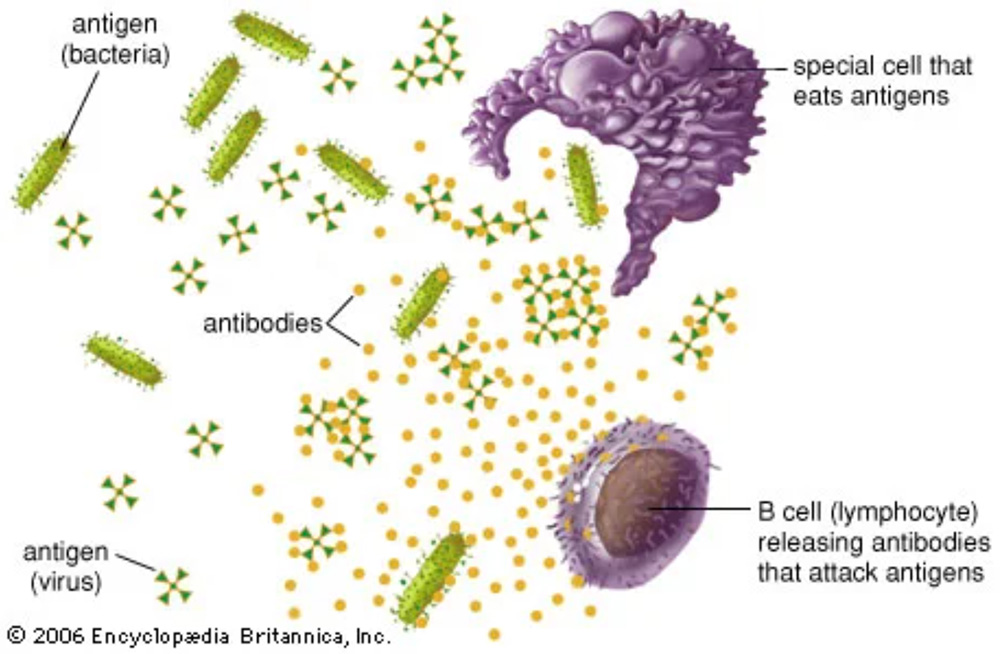
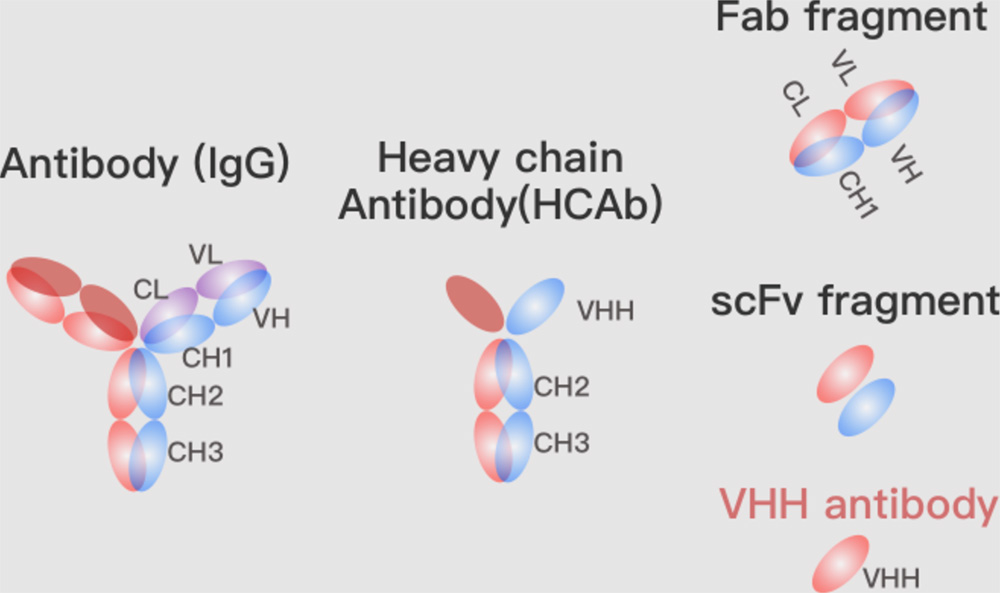
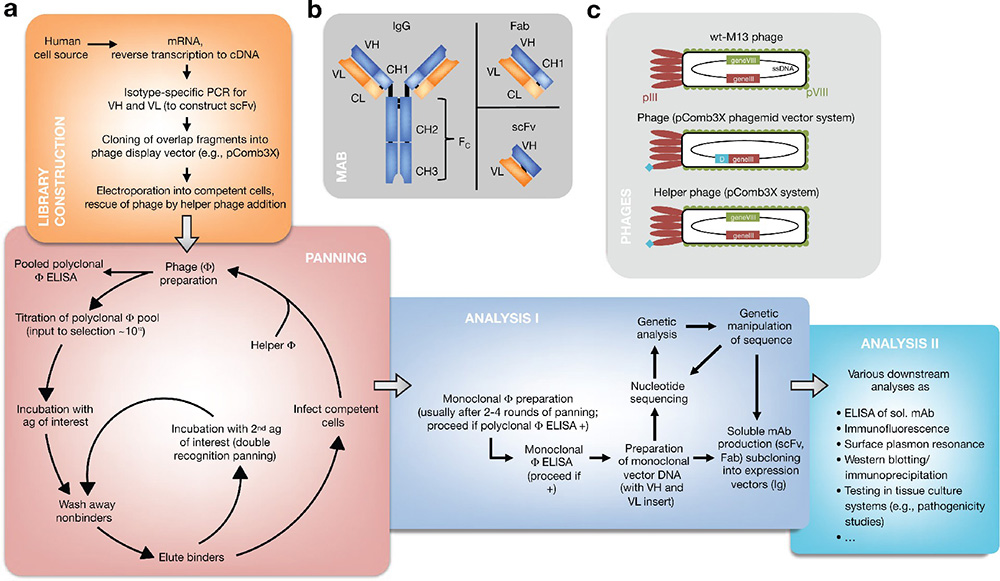
The core functions of antibodies within the immune system are highly diverse and important, serving as the body’s primary defense against a variety of pathogens. These Y-shaped proteins, produced by B cells, are not only tasked with the direct neutralization of pathogens but also play a pivotal role in orchestrating a broader immune response. Through […]
Core Functions of Antibodies Read More »